| HOME |
|---|
SAGITTA
The Arrow
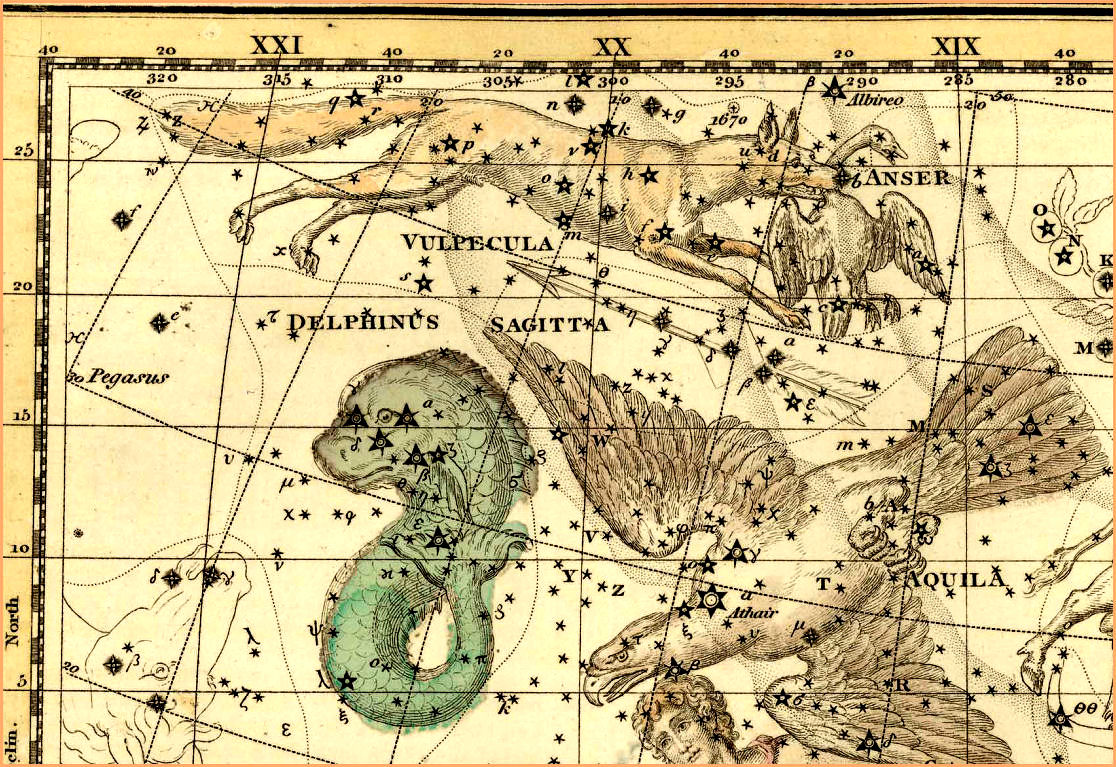
Sagitta - Celestial Atlas by Alexander Jamieson - 1822
| HOME |
|---|

In the crowded depths of the Milky Way, squeezed between Vulpecula the fox, and Aquila the eagle, is the tiny little constellation of Sagitta, the arrow, the third smallest constellation in the sky. Despite its size however, it is one of the most ancient of our constellations, recognized as an arrow by cultures worldwide for about as long as arrows have been around.
The myths and stories surrounding the arrow in the sky are many, but most ancient Greeks thought of Sagitta as the arrow of Eros, the god of love and passion. Eros was the son of Aphrodite (Venus), and Ares (Mars). To the Romans he was known as Cupid, and those who were struck by one of his arrows were filled with romantic love, a legacy of his mother Aphrodite, the goddess of love. Unfortunately the romances did not always go well, for Eros was also the son of Ares, the god of war.
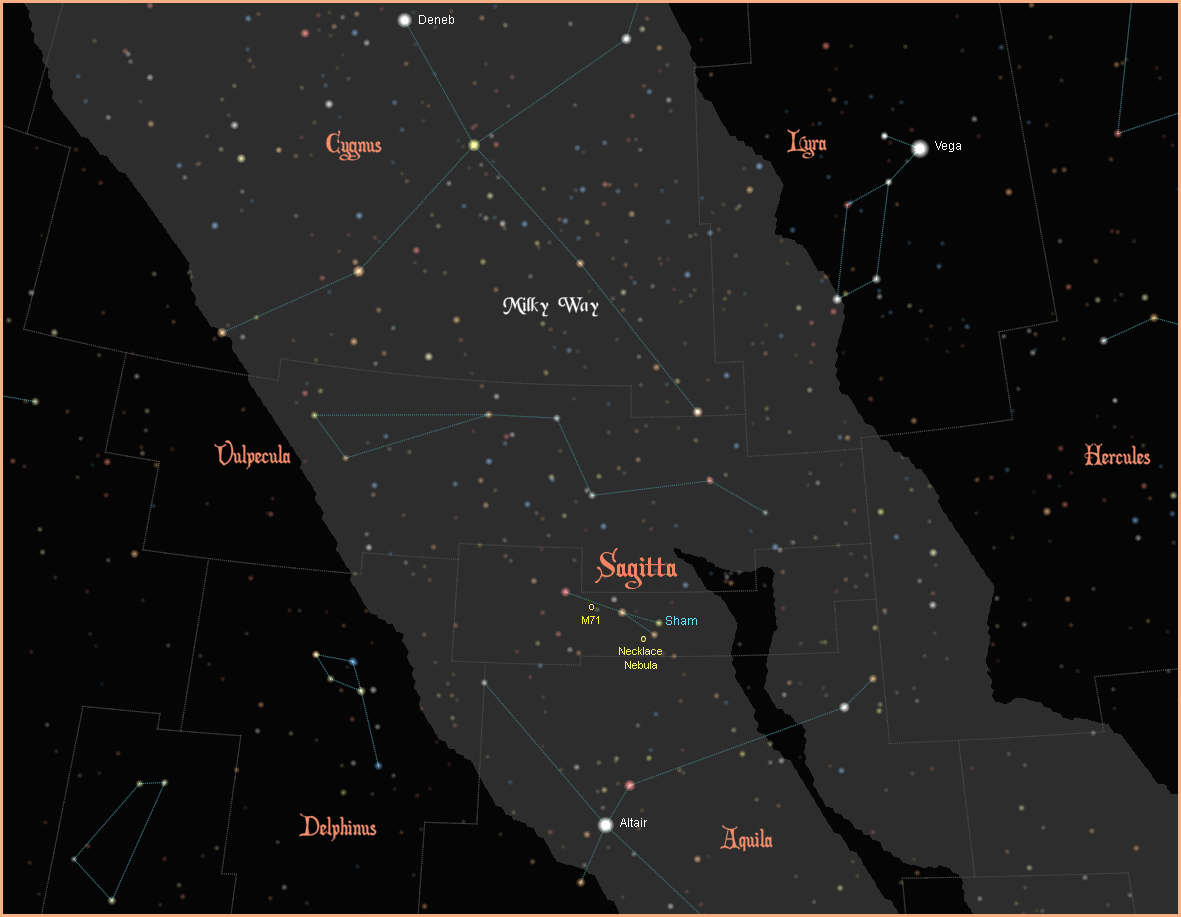
Sagitta has only one named star. It is called Sham. Arabic for arrow. Unconventionally, it is not the brightest star in the constellation. It is only the third brightest, and represents not the point of the arrow, but one of the its feathers, leading to speculation that the star was brighter in ancient times. It is a G1III yellow giant, 610 light years away, with a magnitude of 4.37.
Sagitta has two stars with confirmed planetary systems. The stars are both far away, beyond visual range, and their planets are both gas giants. For more information, visit NASA's New Worlds Atlas.
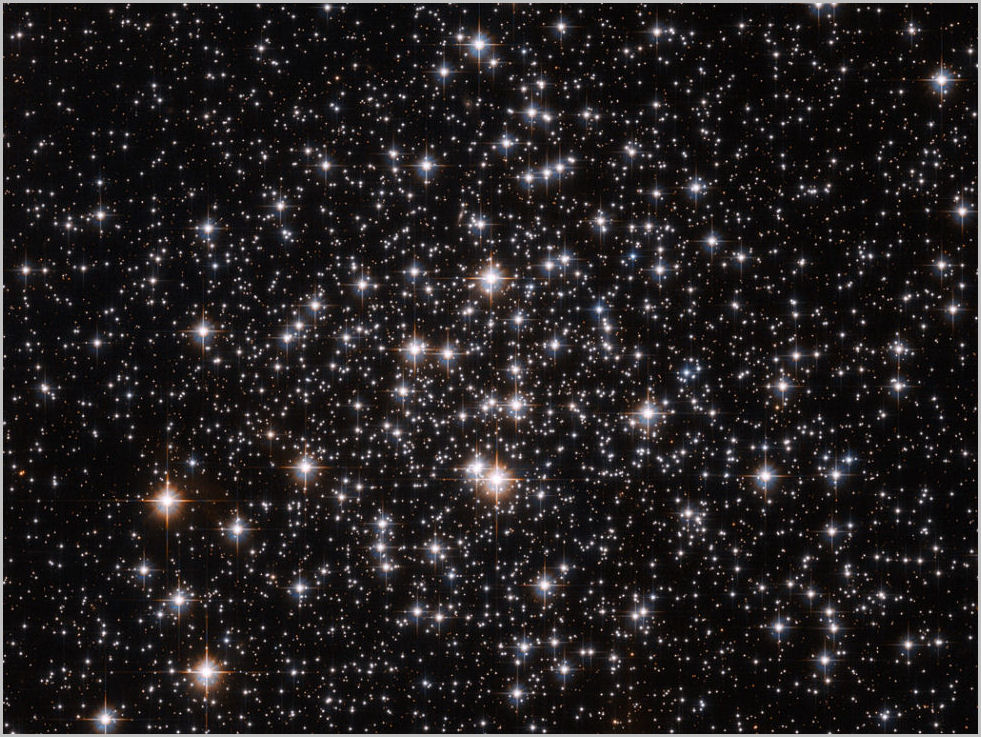
Sagitta has one Messier object: M71, a globular star cluster. With a magnitude of 8.3, it is not visible with the naked eye, but it is a fine sight in a backyard telescope. M71 is 27 light years across, one of the smallest and sparsest of the 200 or so globular star clusters that surround our Milky Way galaxy. It is also one of the closest globular clusters, only 13,000 light years away.

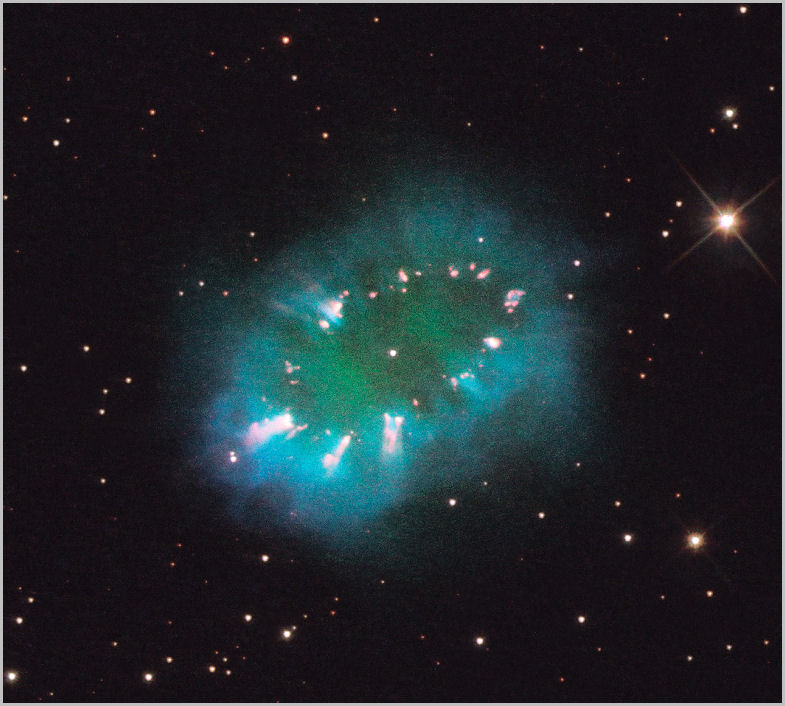
Resembling a giant jewelled necklace suspended in space, is the recently discovered planetary nebula with the cumbersome designation of PN G054.2-03.4. Looking like a planetary disc through smaller telescopes, the eyes of Hubble allow us to see the sparkling jewels of The Necklace Nebula, an expanding cloud of ejected gas from not one but two dying stars at its centre. The bright "jewels" in the necklace are glowing knots of ionized gas. Measuring about two light years across, the nebula is about 15,000 light years away.

|
|
|
|
|
|